The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has emerged as a transformative force in the global business IT landscape, redefining how industries operate, optimize processes, and create value. It integrates physical machinery with digital systems to collect, analyze, and leverage data for more efficient operations.
As industries evolve in response to the digital age, the IIoT is driving innovations that are shaping the future of business IT and propelling companies into the next industrial revolution, often referred to as Industry 4.0.
This article provides a detailed exploration of IIoT, its leading innovations, its impact on business IT, and how it is setting the stage for the future.
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding IIoT: The Intersection of Industry and Connectivity
- 2. Innovations Driven by IIoT in Business IT
- 3. The Role of Security in IIoT Ecosystems
- 4. IIoT and the Future of Business IT
- 5. The Global Impact of IIoT in Industries
- 6. Challenges in Implementing IIoT Solutions
- 7. The Future of IIoT: Trends to Watch
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Understanding IIoT: The Intersection of Industry and Connectivity
1.1. Definition of IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things refers to the application of IoT technologies in industrial settings, particularly in manufacturing, energy, logistics, and transportation. It involves connecting machines, sensors, and devices to the internet to collect and exchange real-time data. This interconnectedness facilitates automation, monitoring, predictive maintenance, and advanced analytics.
IIoT distinguishes itself from consumer IoT by focusing on industrial applications, where reliability, real-time data processing, and system integration are critical. While IoT is more consumer-centric (e.g., smart homes and wearable devices), IIoT is about improving operational efficiency, productivity, and safety in industrial sectors.
1.2. Core Components of IIoT
Several key components define the architecture of IIoT:
- Sensors and Actuators: Sensors gather real-time data (e.g., temperature, pressure, vibration) from machines and industrial environments, while actuators control physical operations.
- Connectivity Protocols: These ensure secure communication between devices, platforms, and applications. Protocols like MQTT, OPC UA, and Bluetooth play vital roles in IIoT ecosystems.
- Edge Computing: Edge devices process data locally, reducing the latency associated with sending all data to cloud-based systems. This is especially critical for industries requiring real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles and robotics.
- Cloud Infrastructure: The cloud acts as the central repository for vast amounts of data, enabling storage, advanced analytics, machine learning, and remote access.
- Analytics Platforms: IIoT generates large datasets, which are analyzed using AI and machine learning to optimize processes, detect anomalies, and predict maintenance needs.
1.3. Difference Between IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) and IoT (Internet of Things)
While IIoT and IoT share the fundamental concept of connecting devices to exchange data, they serve distinct purposes and operate in different environments. Here’s a comparison between the two:
| Aspect | IIoT (Industrial IoT) | IoT (Internet of Things) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connected devices in industries like manufacturing and energy. | Network of devices for consumer and general applications. |
| Application | Used in industries for operations, monitoring, and safety. | Common in smart homes, fitness devices, and smart cities. |
| Scale & Complexity | Large-scale, critical systems like factory machines. | Smaller-scale consumer devices like wearables. |
| Data Usage | Real-time monitoring, automation, and efficiency. | Enhances user experience and automates tasks. |
| Security | High security due to critical operations. | Important but lower risk, mainly personal data security. |
| Latency & Reliability | Requires ultra-low latency and high reliability. | Important but less critical than IIoT. |
| Communication Protocols | Uses industrial protocols like Modbus and OPC-UA. | Uses consumer protocols like Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. |
| Automation Focus | Industrial process automation with minimal human input. | Enhances convenience and lifestyle automation. |
| Cost & Investment | Higher investment for complex infrastructure. | Lower costs, easier to implement. |
| Use Cases | Smart factories, predictive maintenance, power grids. | Smart homes, fitness trackers, connected cars. |
1.4. Key Benefits of IIoT in Business IT
- Improved Operational Efficiency: By automating tasks and optimizing resource use, IIoT reduces downtime and increases overall productivity.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: IIoT enables data-driven decision-making, offering insights that can improve supply chain management, inventory control, and predictive maintenance.
- Cost Reduction: With better insights into operations, businesses can cut costs by reducing waste, minimizing downtime, and optimizing energy use.
- Increased Safety and Compliance: IIoT enhances workplace safety through predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, preventing accidents and ensuring regulatory compliance.
2. Innovations Driven by IIoT in Business IT
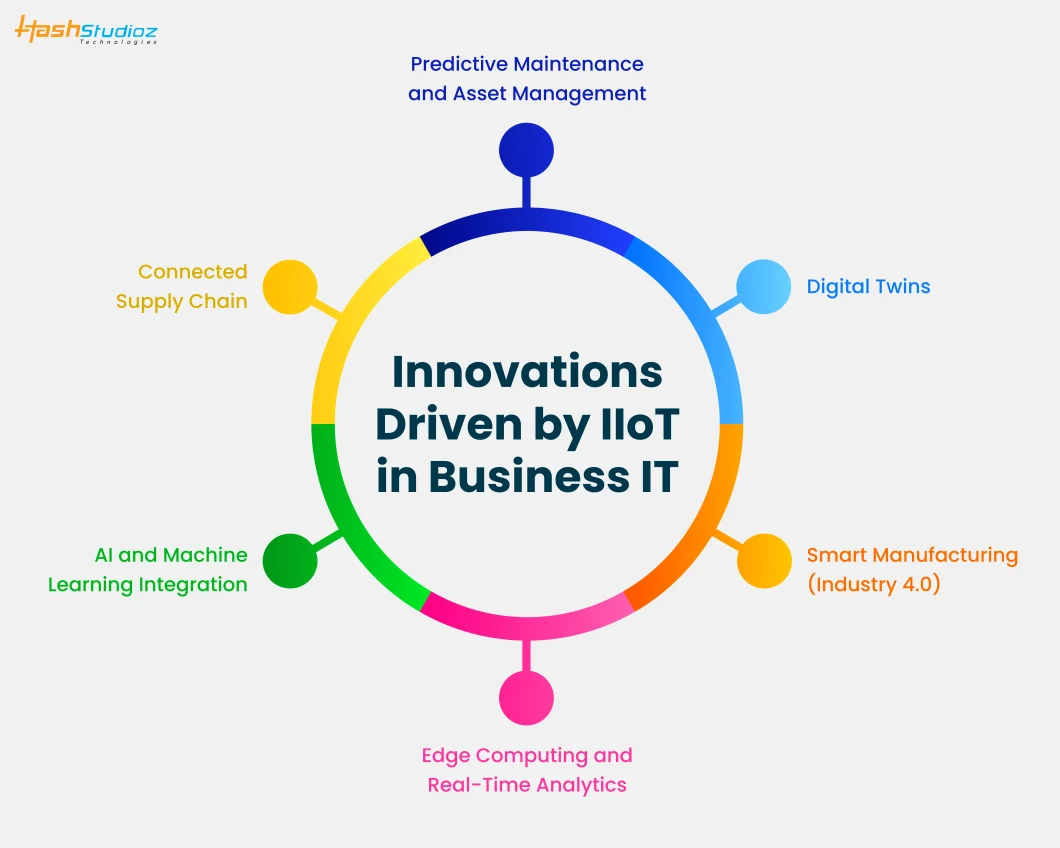
The convergence of IIoT with other emerging technologies is revolutionizing business IT, providing new ways to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and create value. Below are some of the leading innovations facilitated by IIoT:
2.1. Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management
IIoT-powered predictive maintenance uses real-time data from sensors to predict equipment failures before they occur, allowing businesses to service machinery proactively rather than reactively. This is a shift from traditional preventive maintenance strategies, which often result in unnecessary downtime.
- Reduced Downtime: Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned downtime, which can cost industries millions of dollars annually.
- Extended Equipment Lifespan: By identifying potential issues early, businesses can extend the life of their machinery and reduce capital expenditure on new equipment.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Continuous monitoring of assets ensures that businesses can make informed decisions about when to repair, replace, or retire equipment.
2.2. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset, system, or process. In the context of IIoT, digital twins are created using real-time data from sensors attached to machinery or industrial systems. This innovation allows businesses to simulate, monitor, and optimize performance in real-time.
- Enhanced Operational Visibility: Digital twins offer a comprehensive view of operations, helping businesses track the performance and health of their assets.
- Risk Mitigation: By simulating different scenarios, digital twins can identify potential risks, enabling businesses to mitigate them before they impact operations.
- Optimization of Resources: The ability to test different configurations in a virtual environment allows businesses to optimize resource allocation and minimize waste.
2.3. Smart Manufacturing (Industry 4.0)
Smart manufacturing, a key component of Industry 4.0, leverages IIoT to create highly automated and flexible production environments. In smart factories, machines, systems, and humans communicate seamlessly, leading to more efficient, adaptive, and cost-effective operations.
- Automation: IIoT enables the automation of complex tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and allowing businesses to operate around the clock.
- Customization: Smart manufacturing allows for greater customization of products without sacrificing efficiency, making it possible to meet specific customer demands at scale.
- Supply Chain Optimization: With real-time data from every stage of the production process, smart factories can optimize their supply chains to reduce delays, improve inventory management, and enhance logistics.
2.4. Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics
As IIoT generates massive amounts of data, sending all this information to the cloud for processing can create latency issues. Edge computing addresses this by processing data closer to the source, allowing businesses to respond in real-time to changes in their environment.
- Faster Response Times: By processing data locally, edge computing reduces latency and allows for real-time decision-making, which is critical in industries such as autonomous driving and robotics.
- Reduced Bandwidth: By filtering out irrelevant data at the edge, businesses can reduce the amount of data sent to the cloud, lowering costs and improving efficiency.
- Improved Security: With less data traveling over the network, edge computing reduces the risk of data breaches, enhancing the overall security of IIoT systems.
2.5. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are integral to IIoT’s potential. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data generated by IIoT devices and provide actionable insights. Through pattern recognition, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics, AI and ML optimize processes, reduce human error, and unlock new opportunities for innovation.
- Process Optimization: AI models can continuously analyze operational data to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in production processes, helping businesses optimize performance.
- Quality Control: Machine learning algorithms can detect defects and quality issues in real-time, improving product quality and reducing waste.
- Predictive Insights: AI-powered analytics predict trends and potential future issues, helping businesses anticipate market shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
2.6. Connected Supply Chain
IIoT has revolutionized supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility and real-time tracking. Through connected devices and sensors, businesses can monitor every aspect of their supply chain, from raw materials to finished products.
- Improved Transparency: Real-time data provides visibility into each step of the supply chain, allowing businesses to track inventory levels, monitor shipments, and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Enhanced Collaboration: IIoT facilitates seamless communication between different players in the supply chain, fostering better collaboration and reducing the likelihood of delays or disruptions.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: With greater control over logistics, businesses can reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions, leading to more sustainable supply chain operations.

3. The Role of Security in IIoT Ecosystems
As IIoT continues to expand, security becomes an increasingly important concern. The interconnected nature of IIoT devices and systems creates multiple points of vulnerability, making it essential to implement robust security measures to protect data and operations.
3.1. Common Security Challenges in IIoT
- Increased Attack Surface: The sheer number of connected devices in an IIoT environment increases the attack surface, making it more difficult to secure the entire system.
- Data Privacy and Integrity: The real-time data generated by IIoT devices is often sensitive, making data privacy and integrity a top priority for businesses.
- Legacy Systems: Many industrial systems were not designed with security in mind, making it difficult to integrate modern security measures without significant upgrades.
3.2. Best Practices for IIoT Security
- End-to-End Encryption: Encrypting data at every stage of transmission ensures that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access.
- Secure Device Authentication: Ensuring that only authorized devices can connect to the IIoT network reduces the risk of unauthorized access or tampering.
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping IIoT devices and systems up to date with the latest security patches is critical for mitigating vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: By dividing the IIoT network into smaller segments, businesses can contain potential breaches and prevent them from spreading to other parts of the system.
4. IIoT and the Future of Business IT
As IIoT continues to evolve, its impact on business IT will only become more profound. The integration of AI, edge computing, and other advanced technologies is driving new levels of innovation and efficiency, positioning IIoT as a critical component of the future industrial landscape.
4.1. Scalability and Interoperability
For IIoT to continue to drive innovation, businesses must focus on scalability and interoperability. As IIoT ecosystems grow, it becomes essential to ensure that devices, platforms, and applications can seamlessly communicate and scale with the needs of the business.
4.2. Sustainability and IIoT
The integration of IIoT with sustainable business practices is expected to grow, particularly in energy management, waste reduction, and resource optimization. IIoT will play a pivotal role in helping businesses meet sustainability goals by offering real-time insights into resource consumption and enabling more efficient operations.
4.3. Adoption Barriers and Industry Challenges
Despite the immense potential of IIoT, several challenges remain. High implementation costs, a lack of standardized protocols, and the complexity of integrating IIoT with legacy systems can slow adoption. However, as technology continues to evolve, these barriers are likely to diminish, making IIoT accessible to a broader range of industries.
How Can You Accelerate Hyperautomation with Industrial IoT Adoption?
4.4. The Role of Data in Driving Business Growth
One of the most transformative elements of IIoT is its ability to generate vast amounts of data. The insights gained from this data are reshaping how businesses make decisions, manage operations, and create value. This data-driven approach is not only improving operational efficiency but also fostering innovation across industries.
4.4.1 Data-Driven Decision Making
IIoT-enabled data analytics allows businesses to move from traditional decision-making processes, which often relied on intuition or historical patterns, to a more precise and real-time approach. This capability enables organizations to identify trends, make informed predictions, and respond quickly to changes in the business environment.
- Operational Insights: IIoT data provides detailed insights into various aspects of production, logistics, and resource management, empowering leaders to optimize performance and increase productivity.
- Customer-Centric Innovations: By analyzing data related to consumer behavior, demand patterns, and product performance, businesses can tailor their offerings and improve customer experiences.
4.4.2 Enhanced Business Agility
Data-driven insights enable businesses to be more agile in responding to market dynamics. With the ability to monitor real-time performance, companies can quickly identify inefficiencies or emerging trends and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Real-Time Monitoring: IIoT systems allow for continuous monitoring of production lines, supply chains, and operations, enabling quick intervention in case of malfunctions or changes in demand.
- Rapid Adaptation: Data analytics powered by IIoT allows businesses to pivot quickly, whether that means adjusting production volumes, shifting logistics strategies, or launching new products.
4.4.3 Driving Innovation with AI and Machine Learning
The intersection of AI, machine learning, and IIoT is a significant driving force behind business innovation. By analyzing complex data sets, AI and machine learning algorithms provide predictive insights that can lead to more efficient operations, enhanced product quality, and the development of new business models.
- Product Innovation: Machine learning can analyze customer usage patterns and product performance data to guide the development of next-generation products and services.
- Process Automation: AI-driven automation reduces manual interventions and streamlines workflows, making operations more scalable and less prone to human error.
5. The Global Impact of IIoT in Industries
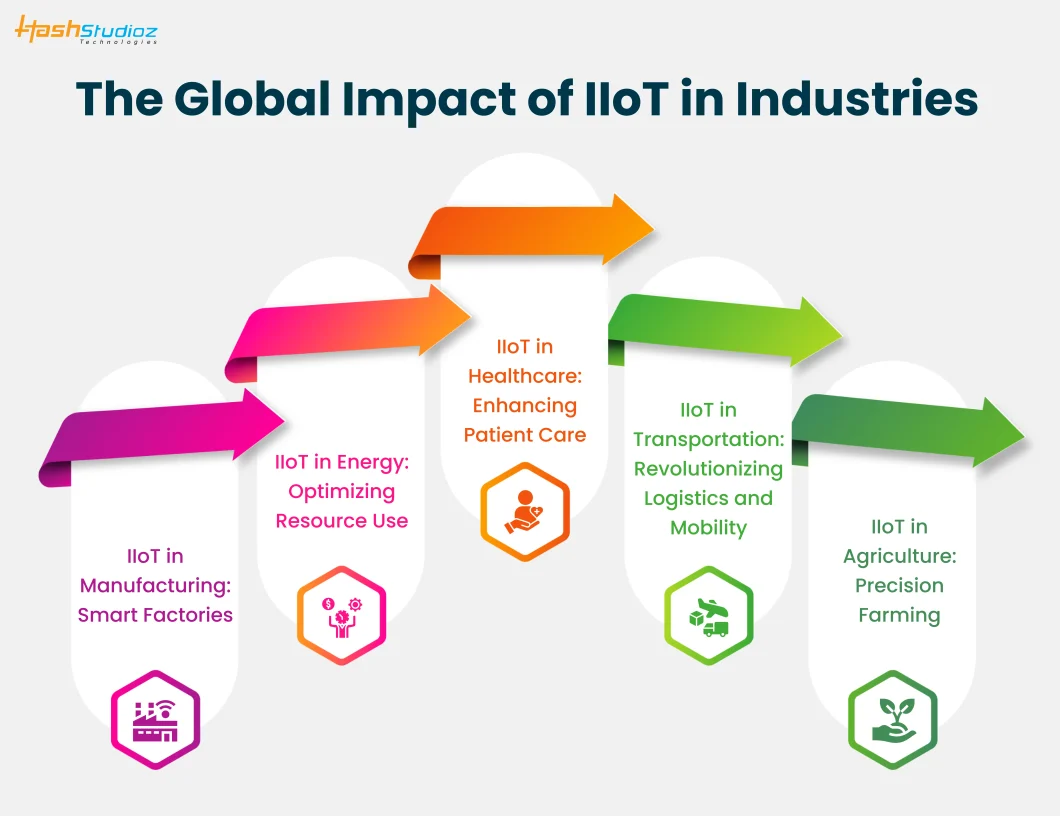
IIoT is impacting industries worldwide, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, energy, healthcare, and transportation. The transformation is global, and its influence on different industries is profound.
5.1 IIoT in Manufacturing: Smart Factories
Manufacturing is perhaps the most visible beneficiary of IIoT technology. The concept of “smart factories,” where machines, devices, and people are connected in a highly automated environment, has transformed the manufacturing sector.
- Automation and Robotics: In smart factories, robots and automated systems handle routine tasks, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
- Real-Time Monitoring: IIoT allows for the real-time monitoring of production lines, helping manufacturers maintain quality control and reduce waste.
- Customization at Scale: IIoT also enables manufacturers to offer customized products without sacrificing the benefits of mass production. By leveraging real-time data and flexible automation, smart factories can adjust production runs to meet specific customer needs.
5.2 IIoT in Energy: Optimizing Resource Use
The energy sector is undergoing a transformation as IIoT technologies are applied to improve efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and increase operational reliability. Smart grids, renewable energy management, and advanced monitoring systems are key IIoT applications in this field.
- Smart Grids: IIoT-powered smart grids enable utilities to balance supply and demand dynamically, ensuring that electricity is distributed more efficiently. This reduces energy waste and supports the integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar.
- Energy Efficiency: IIoT sensors provide real-time data on energy consumption, allowing businesses to optimize their use of resources and reduce operational costs.
- Predictive Maintenance in Power Plants: In power generation, predictive maintenance systems ensure that critical equipment like turbines and transformers operate efficiently, reducing downtime and extending the life of the infrastructure.
5.3 IIoT in Healthcare: Enhancing Patient Care
The healthcare sector is another area where IIoT is making a significant impact. By integrating connected medical devices, healthcare providers can offer more personalized, efficient, and cost-effective care.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: IIoT enables real-time vital sign monitoring for early issue detection and timely care.
- Improved Hospital Management: IIoT tracks hospital resources to optimize use and prevent shortages.
- Smart Medical Devices: Connected medical devices enable real-time monitoring and faster, accurate treatment.
5.4 IIoT in Transportation: Revolutionizing Logistics and Mobility
In the transportation and logistics sector, IIoT is reshaping how goods and people move. By enabling real-time tracking, predictive maintenance, and automation, IIoT improves efficiency, reduces costs, and enhances the overall customer experience.
- Fleet Management: IIoT-enabled fleet management systems provide real-time insights into vehicle performance, fuel consumption, and driver behavior, allowing businesses to optimize logistics operations.
- Predictive Maintenance for Vehicles: Similar to its application in manufacturing, IIoT can predict vehicle maintenance needs, reducing breakdowns and ensuring that transport schedules are met.
- Smart Cities: IIoT is also integral to the development of smart cities, where connected infrastructure such as traffic lights, public transportation, and parking systems are managed in real-time to improve mobility and reduce congestion.
5.5 IIoT in Agriculture: Precision Farming
Agriculture, one of the oldest industries, is undergoing a technological revolution driven by IIoT. IIoT-powered precision farming enables real-time monitoring for smarter, sustainable agriculture.
- Crop Monitoring: IIoT sensors can monitor soil moisture, nutrient levels, and other critical variables, ensuring that crops receive the exact amount of water and nutrients they need.
- Automated Farming Equipment: IIoT enables automated machinery, such as drones and tractors, to perform tasks like planting, harvesting, and spraying with minimal human intervention.
- Yield Optimization: With real-time data on crop conditions, farmers can optimize planting and harvesting schedules, leading to higher yields and more efficient use of land.

6. Challenges in Implementing IIoT Solutions
While IIoT offers numerous benefits, businesses face several challenges in implementing and managing IIoT systems. These challenges, if not properly addressed, can slow down adoption and limit the full potential of IIoT in transforming industries.
6.1 Interoperability Issues
One of the significant challenges with IIoT adoption is interoperability. IIoT ecosystems often consist of devices and systems from different manufacturers, each with its own protocols and standards. Ensuring that all these components can communicate seamlessly is a major technical hurdle.
- Standardization: There is a growing need for standardized communication protocols that allow different IIoT devices to work together efficiently.
- Vendor Lock-In: Companies should avoid vendor lock-in to ensure scalability and flexibility.
6.2 Data Management
The sheer volume of data generated by IIoT devices presents challenges in terms of storage, processing, and analysis. Managing this data effectively is critical to unlocking the full value of IIoT.
- Data Overload: Businesses must implement robust data management strategies to handle the influx of data generated by IIoT systems.
- Real-Time Processing: Processing and analyzing IIoT data in real-time requires advanced analytics platforms, edge computing solutions, and scalable cloud infrastructure.
6.3 Cost and Complexity of Implementation
Deploying IIoT solutions can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. The cost of sensors, connectivity, analytics platforms, and infrastructure upgrades can quickly add up.
- Upfront Investment: The initial investment required for IIoT implementation can be a barrier for businesses with limited capital.
- Complex Integration: Integrating IIoT with legacy systems is complex and may require major IT upgrades.
6.4 Security Risks
As IIoT systems involve the connection of numerous devices and machines, the risk of cyberattacks increases significantly. Securing IIoT systems is a critical challenge, given the diverse range of devices and the complexity of the networks involved.
- Vulnerable Endpoints: IIoT devices, especially older or low-cost ones, may not have adequate security features, making them vulnerable to attacks.
- Data Breaches: IIoT real-time data is sensitive, demanding strong encryption and access controls.
7. The Future of IIoT: Trends to Watch
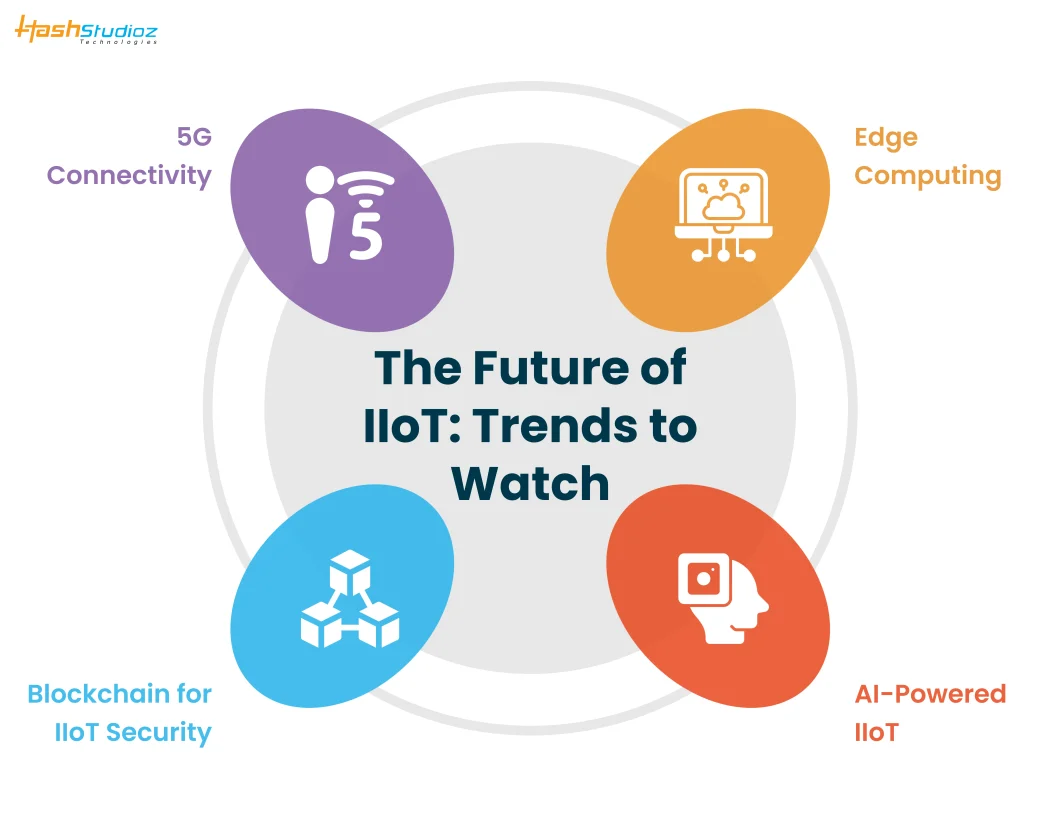
As IIoT technology continues to evolve, several key trends are shaping its future and driving innovation in the business IT sphere. These trends indicate how IIoT will continue to transform industries and enable new possibilities for businesses.
7.1 5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks is expected to be a game-changer for IIoT. With its ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and ability to support a massive number of connected devices, 5G will significantly enhance IIoT applications.
- Real-Time Processing: 5G will enable faster data transmission, improving the responsiveness of IIoT systems in applications like autonomous vehicles and smart cities.
- Enhanced Device Connectivity: The ability to connect more devices simultaneously will drive the expansion of IIoT ecosystems, particularly in large-scale industrial environments.
7.2 Edge Computing
Edge computing, which processes data closer to the source of generation rather than relying on centralized cloud servers, is gaining traction in IIoT applications. This approach reduces latency and enables faster decision-making.
- Faster Data Processing: By processing data at the edge, businesses can react to changes in real-time, without the delays associated with cloud-based analytics.
- Reduced Bandwidth Usage: Edge computing reduces the need to transmit large volumes of data to the cloud, lowering bandwidth costs and improving overall efficiency.
7.3 AI-Powered IIoT
AI will drive IIoT in predictive maintenance, automation, and anomaly detection. AI’s ability to analyze large datasets and identify patterns will enhance the capabilities of IIoT systems.
- Smart Maintenance: AI-driven algorithms will predict equipment failures with even greater accuracy, reducing downtime and extending asset life.
- Autonomous Systems: AI-driven drones and robots will enhance IIoT by handling monitoring, inspection, and repairs autonomously.
7.4 Blockchain for IIoT Security
Blockchain technology offers a promising solution for enhancing the security of IIoT systems. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain can ensure that data is securely stored and transmitted across IIoT networks.
- Data Integrity: Blockchain secures IIoT data, ensuring tamper-proof information flow.
- Decentralized Security: Blockchain enhances IIoT security by eliminating central authority risks.
Conclusion
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing business IT by enhancing connectivity, data insights, and automation. Key to this transformation are Industrial IoT Gateway Solutions, which ensure seamless communication between IIoT devices and networks, enabling secure and efficient data flow. Despite challenges like interoperability and security, advancing technologies such as 5G and edge computing promise a bright future for IIoT. Embracing these innovations positions businesses to excel in the evolving digital landscape, boosting growth and sustainability.
At HashStudioz, we specialize in delivering cutting-edge Industrial IoT (IIoT) gateway solutions that enhance connectivity, data integration, and operational efficiency. Our innovative gateways bridge the gap between industrial systems and cloud platforms, enabling seamless data flow and real-time insights. With a focus on reliability and scalability, HashStudioz empowers businesses to harness the full potential of IIoT for smarter, more efficient operations. Explore how our tailored solutions can transform your industrial processes today.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the use of interconnected sensors, devices, and machines in industrial settings to collect, exchange, and analyze data. This technology enables real-time monitoring, automation, and data-driven decision-making, enhancing efficiency, productivity, and safety in industries such as manufacturing, energy, healthcare, and transportation.
2. How does IIoT improve operational efficiency?
IIoT improves operational efficiency by providing real-time data on machinery, production processes, and supply chains. This data allows for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and equipment failures, optimizing resource usage, and automating routine tasks. By enabling faster decision-making and minimizing waste, IIoT helps organizations streamline their operations and reduce costs.
3. What are the key challenges businesses face when implementing IIoT?
Some of the main challenges businesses face when implementing IIoT include interoperability issues between different devices and systems, managing and analyzing the large volume of data generated by IIoT devices, the high cost of initial investment, and ensuring adequate cybersecurity to protect against data breaches and cyberattacks.
4. How does IIoT contribute to business growth?
IIoT drives business growth by enabling data-driven decision-making, improving product quality, and optimizing operations. It provides valuable insights into customer behavior and operational performance, allowing businesses to innovate and create more personalized products. Additionally, IIoT helps companies stay agile, adapt to market changes quickly, and enhance customer satisfaction.
5. What industries benefit the most from IIoT?
IIoT benefits industries like manufacturing, energy, healthcare, transportation, and agriculture. Each of these sectors uses IIoT to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve operational accuracy and sustainability.

