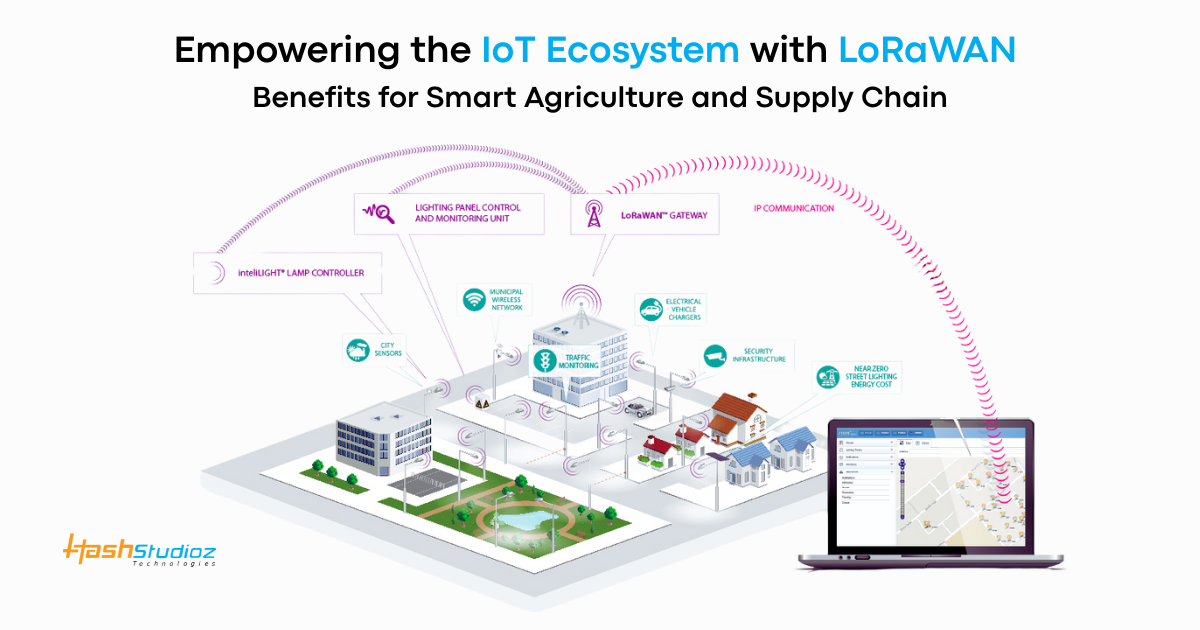
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming industries across the globe. Agriculture and supply chain management are two sectors that benefit the most from these changes. Among the various IoT communication technologies, LoRaWAN for IoT Ecosystem stands out due to its long-range capabilities, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness.
LoRaWAN Solutions have become a critical part of smart agriculture and supply chain systems. Their adoption is growing fast, with IoT Analytics predicting that there will be over 27 billion connected IoT devices by 2025. LoRaWAN-Based Solutions are helping to build reliable and scalable ecosystems that meet the needs of modern businesses.
Table of Contents
- Understanding LoRaWAN Technology
- Benefits of LoRaWAN in Smart Agriculture
- Benefits of LoRaWAN in Supply Chain Management
- Why LoRaWAN is Suitable for Agriculture and Supply Chains
- Technical Challenges and Solutions
- Real-World Use Cases
- Future Outlook
- The Rise of LoRaWAN Technology
- Partner with HashStudioz for Next-Generation LoRaWAN Solutions
- Conclusion
Understanding LoRaWAN Technology
LoRaWAN stands for Long Range Wide Area Network. It is a wireless communication protocol designed for low-power devices that operate over long distances. LoRaWAN uses the LoRa modulation technique, which allows devices to transmit small amounts of data at very low data rates.
Key Features of LoRaWAN
- Long Range: LoRaWAN devices can communicate over distances up to 15 kilometers in rural areas.
- Low Power: Devices can run for years on small batteries.
- High Capacity: One LoRaWAN gateway can support thousands of devices.
- Secure: It provides end-to-end encryption at the network and application layers.
- Cost-Effective: Low infrastructure and maintenance costs compared to cellular networks.
These features make LoRaWAN-Based Solutions ideal for applications that require widespread coverage and energy efficiency.
Benefits of LoRaWAN in Smart Agriculture
Smart agriculture uses IoT devices to monitor and manage farm operations. LoRaWAN Solutions play a major role in this sector by providing reliable communication between sensors, machines, and management platforms.
1. Soil and Crop Monitoring
Sensors equipped with LoRaWAN technology can monitor soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient levels. This data helps farmers adjust irrigation and fertilization schedules.
Example: A study by the University of Nebraska showed that real-time soil monitoring could reduce water usage by up to 35%.
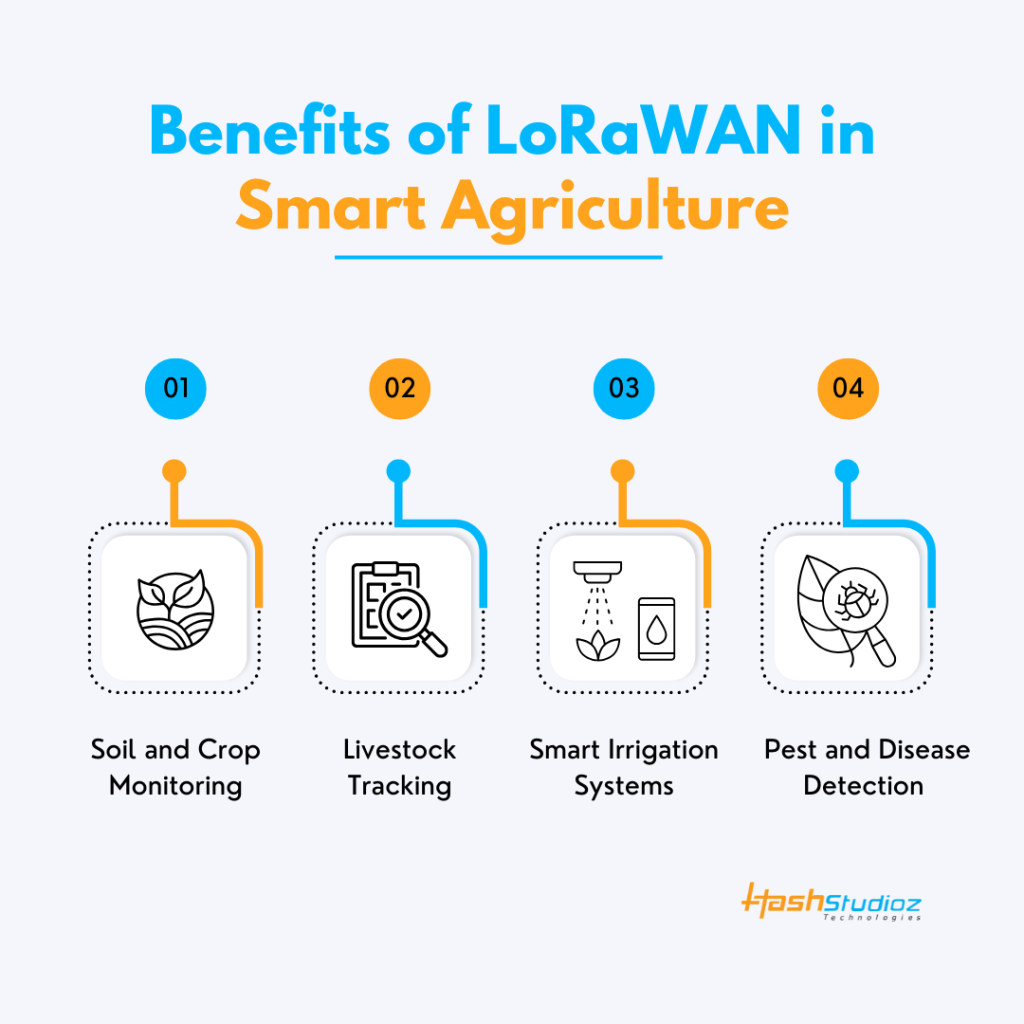
2. Livestock Tracking
Farmers use LoRaWAN-Based Solutions to track livestock movements. Wearable devices monitor animal health indicators like heart rate, activity levels, and location.
Fact: According to MarketsandMarkets, the smart livestock monitoring market is expected to reach $2.5 billion by 2026, largely driven by IoT technologies like LoRaWAN.
3. Smart Irrigation Systems
LoRaWAN enables automated irrigation systems that activate based on real-time soil and weather data. This optimizes water usage and improves crop yields.
Example: Farmers in Spain’s Valencia region reported a 25% increase in crop yields after adopting LoRaWAN-based smart irrigation.
4. Pest and Disease Detection
Sensors detect early signs of pest infestation or plant diseases. Farmers receive instant alerts, allowing for early intervention.
Benefit: Early action reduces pesticide use, lowers costs, and improves crop quality.
Benefits of LoRaWAN in Supply Chain Management
Supply chains are complex systems that involve multiple stakeholders, assets, and processes. LoRaWAN Solutions provide real-time data that enhances visibility, efficiency, and decision-making.
1. Asset Tracking
LoRaWAN-Based Solutions help track shipments, containers, and pallets throughout the supply chain. Devices monitor location, temperature, humidity, and movement.
Fact: DHL reports that real-time tracking solutions can reduce shipment delays by 60%.
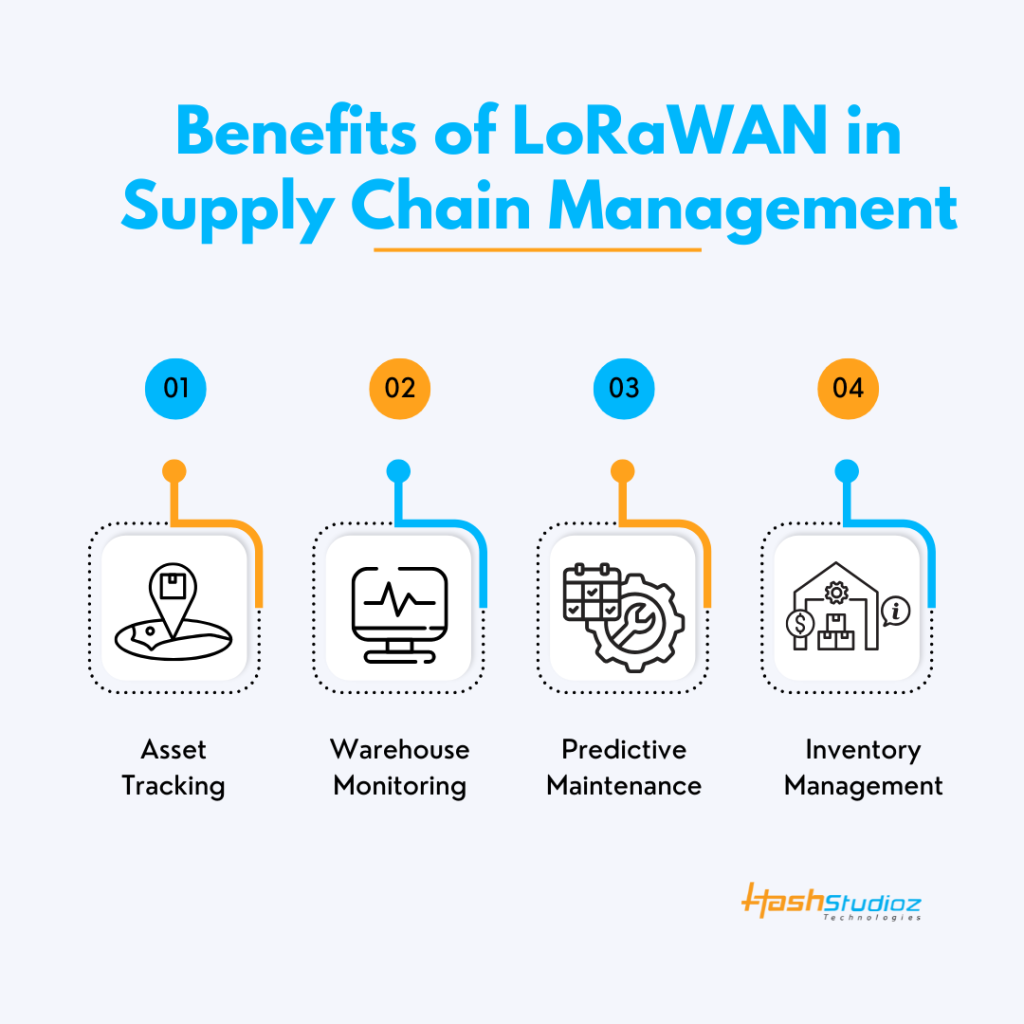
2. Warehouse Monitoring
LoRaWAN sensors monitor environmental conditions inside warehouses. These include temperature, humidity, air quality, and lighting.
Example: Food warehouses use LoRaWAN to ensure that perishable goods stay within safe temperature ranges. This helps meet regulatory compliance and reduce spoilage.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Sensors attached to machines collect operational data. This information predicts when maintenance is needed before a breakdown occurs.
Benefit: Predictive maintenance reduces equipment downtime by up to 30%, according to McKinsey Global Institute.
4. Inventory Management
IoT devices using LoRaWAN help in tracking inventory levels in real-time. This reduces the risk of overstocking or stockouts.
Example: A logistics company in Germany reported a 20% reduction in inventory costs after deploying a LoRaWAN-based tracking system.
Why LoRaWAN is Suitable for Agriculture and Supply Chains
Several technical advantages make LoRaWAN-Based Solutions the best choice for these industries.
1. Scalability
One LoRaWAN gateway can connect thousands of devices. This is important for large farms and supply chain networks.
2. Energy Efficiency
Agriculture sensors and supply chain trackers often need to operate in remote areas without access to constant power. LoRaWAN devices consume very little energy, allowing them to run on batteries for years.
3. Cost Savings
Deploying LoRaWAN infrastructure is cheaper compared to setting up cellular networks. This makes it accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
4. Robustness
LoRaWAN networks perform well even in harsh environments, such as fields, warehouses, and transportation routes.
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Despite its many benefits, implementing LoRaWAN Solutions comes with challenges. However, advances in technology continue to address these issues.
1. Network Interference
Operating in unlicensed frequency bands can lead to signal interference. The solution lies in adaptive data rates and network management tools that optimize transmissions.
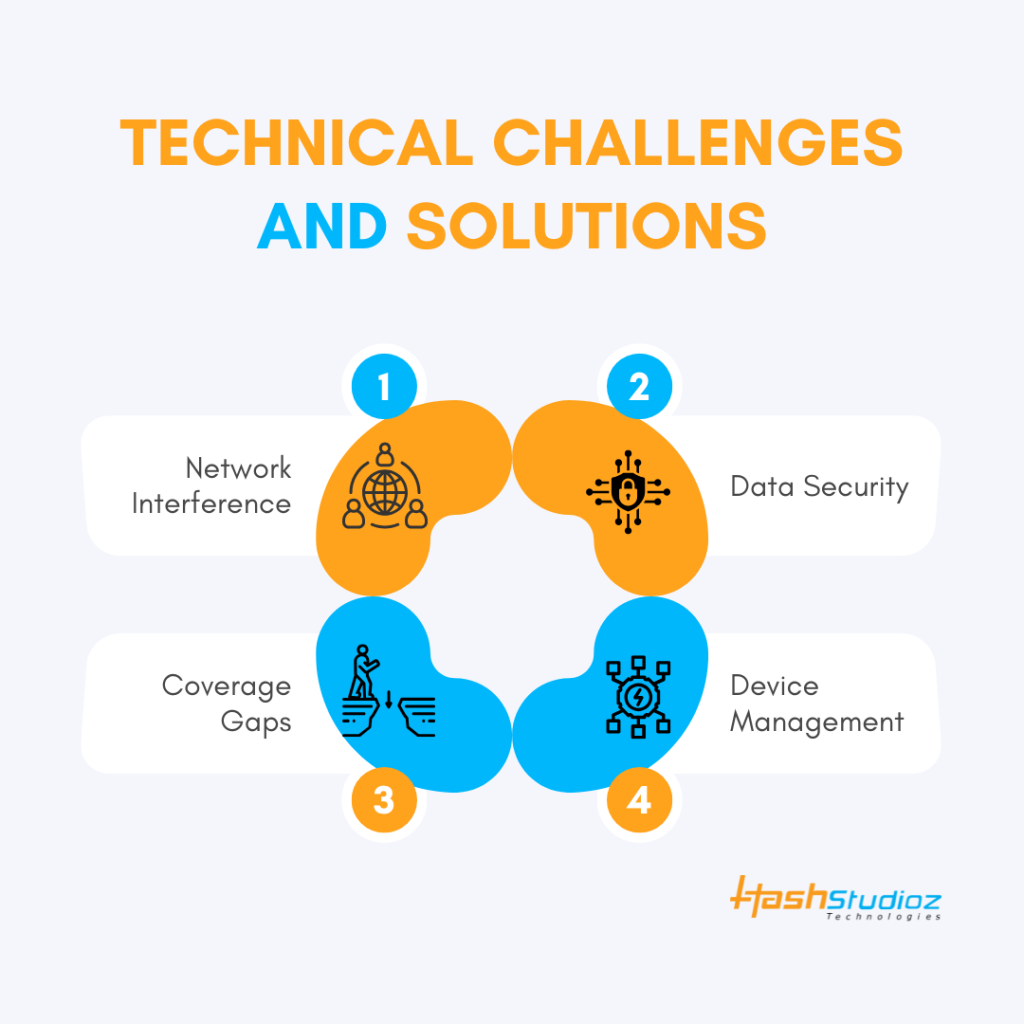
2. Data Security
Since IoT devices handle sensitive data, security is critical. LoRaWAN offers built-in encryption, but businesses must also secure endpoints and servers.
3. Coverage Gaps
In some remote areas, gateway coverage might be limited. Hybrid networks using LoRaWAN and satellite links can help extend connectivity.
4. Device Management
Managing thousands of devices can be difficult. Modern IoT platforms offer automated device onboarding, remote updates, and maintenance tools.
Real-World Use Cases
1. Smart Vineyards in Italy
Several vineyards in Italy use LoRaWAN Solutions for soil monitoring, frost alerts, and irrigation management. This has improved grape quality and increased wine production by 15%.
2. Cold Chain Monitoring in the USA
Pharmaceutical companies in the USA use LoRaWAN sensors to monitor temperature-sensitive vaccines during transportation. Real-time alerts help prevent spoilage and ensure compliance with regulations.
3. Crop Insurance in India
Insurance companies in India deploy LoRaWAN devices to collect weather and soil data. This data is used to offer more accurate and affordable crop insurance to farmers.
Future Outlook
The adoption of LoRaWAN Solutions is set to increase rapidly over the next few years. Industry analysts predict that the global LoRaWAN market will surpass $25 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by the need for efficient, low-power, and long-range communication technologies across agriculture, supply chains, and other industries.
Several important trends are shaping the future of LoRaWAN-Based Solutions:
1. Integration with AI for Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming a crucial part of IoT systems. When combined with LoRaWAN networks, AI can analyze vast amounts of data collected from sensors in real time. This enables predictive analytics, where future events and system behaviors are forecasted based on current and historical data.
In agriculture, AI models can predict irrigation needs, pest outbreaks, or optimal harvest times by studying data from LoRaWAN-enabled soil and weather sensors. In supply chains, predictive analytics helps forecast equipment failures, optimize shipping routes, and prevent delays before they occur.
Fact: According to IDC, by 2026, over 75% of enterprises will have AI-powered IoT systems to improve operational efficiency.
2. Use of Blockchain for Secure Supply Chain Transactions
Security and transparency are major concerns in supply chain management. Blockchain technology provides a decentralized, tamper-proof way of recording transactions and data exchanges.
When integrated with LoRaWAN Solutions, blockchain can verify the origin, location, and handling conditions of goods throughout the supply chain. Every sensor reading, from temperature logs to location updates, can be securely recorded in a blockchain ledger. This ensures that stakeholders can trust the data and trace the entire journey of a product.
Example: Pharmaceutical companies are using LoRaWAN devices and blockchain to track vaccine shipments, ensuring that temperature conditions are maintained and documented securely.
3. Expansion of Hybrid Communication Networks
While LoRaWAN provides excellent coverage for most rural and urban areas, some regions remain challenging due to geographical barriers or infrastructure limitations. To overcome this, hybrid communication networks are emerging.
These networks combine LoRaWAN with 5G and satellite communication. LoRaWAN handles local, low-power transmissions, while 5G and satellites manage backhaul communication or fill coverage gaps.
This hybrid approach allows continuous and reliable monitoring across large distances, even in remote agricultural fields, deep forests, or vast ocean transport routes.
Fact: Research by ABI Research forecasts that hybrid IoT connectivity solutions will account for 40% of all IoT deployments by 2030.
The Rise of LoRaWAN Technology
LoRaWAN is a protocol for low-power, wide-area networks (LPWAN) designed to enable long-range communication for IoT devices. The protocol is especially known for its ability to connect a vast number of devices over large distances while maintaining minimal power consumption. This makes LoRaWAN ideal for applications in rural areas, smart cities, and industries requiring long-range communication between sensors and actuators.
LoRaWAN technology has matured over the years, and as the IoT landscape expands, the need for more sophisticated and reliable solutions has never been higher. Let’s dive into the key areas where LoRaWAN-based solutions are evolving:
1. Increased Energy Efficiency
A. The Challenge of Power Consumption
One of the major appeals of LoRaWAN has always been its energy efficiency. However, as more IoT devices are deployed, the need for better energy management becomes increasingly important. Many IoT devices are placed in remote or hard-to-reach locations, where regular battery replacements are costly, impractical, and unsustainable.
B. New Chip Designs
New developments in semiconductor technology are pushing the boundaries of energy-efficient design. LoRaWAN chips are becoming smaller, more efficient, and less power-hungry. Modern chips are designed to operate in low-power modes for extended periods, even while maintaining a constant connection to the network.
Manufacturers are also integrating power-saving features such as dynamic power scaling, which adjusts the power consumption based on the device’s activity level. These chips allow IoT devices to consume less power during idle times, extending their battery life significantly.
C. Energy Harvesting Technologies
Energy harvesting is another innovation that is significantly improving the sustainability of LoRaWAN-based solutions. By capturing energy from environmental sources, such as solar, wind, or vibrations, devices can recharge their batteries or even operate without needing batteries at all. This technology will reduce the need for battery replacements and make LoRaWAN devices more suitable for long-term deployment in remote areas.
For example, agricultural sensors deployed in fields can be powered by solar energy, ensuring they continue to operate throughout the year without requiring regular battery changes. Energy harvesting could also be applied to sensors in factories or warehouses, where kinetic energy from machinery could power IoT devices.
2. Greater Scalability
A. Managing Millions of Devices
One of the core advantages of LoRaWAN is its ability to support a large number of devices in a wide geographical area. However, as IoT deployments grow, managing networks with millions of devices can become challenging.
LoRaWAN-based solutions need robust network management platforms that can handle the complexities of scaling these deployments. The evolution of LoRaWAN network management platforms will focus on simplifying the administration and monitoring of large-scale IoT deployments, making it easier for companies to manage millions of devices.
B. Advanced Network Management Platforms
Next-generation network management platforms will introduce improved features such as:
- Automatic Network Optimization: These platforms will automatically adjust network configurations to optimize performance as new devices are added. This includes managing the allocation of communication channels and network resources to ensure minimal interference and maximum reliability.
- Device Management: As the number of devices grows, managing device firmware, configurations, and updates will become more complex. The new platforms will support automatic over-the-air (OTA) updates, ensuring that all devices are running the latest software and security patches.
- Seamless Connectivity: Future LoRaWAN networks will support the dynamic handoff of devices between gateways and networks without disruption. This is particularly important for large-scale deployments where devices may be spread across vast geographic areas.
3. Enhanced Security
A. The Growing Threat of Cybersecurity
As the number of IoT devices connected to the internet increases, so does the potential for cyber threats. Many of the current LoRaWAN-based solutions have security features, but as they become more widespread and integrated into critical infrastructure, advanced security measures will be essential to protect sensitive data and ensure the integrity of the network.
B. Advanced Encryption Standards
LoRaWAN already employs AES-128 encryption for securing data transmission between devices and gateways. However, future LoRaWAN-based solutions will adopt more robust encryption standards, such as quantum-resistant encryption, to safeguard against future security threats.
Quantum computing could pose a serious threat to traditional encryption methods, and as this technology becomes more viable, LoRaWAN networks will need to evolve to incorporate quantum-resistant algorithms to protect their communications from potential cyberattacks.
C. Device Authentication
As the number of devices on a network grows, ensuring the authenticity of each device becomes more challenging. Advanced device authentication mechanisms will be integrated into LoRaWAN solutions to ensure that only authorized devices can access the network. This will be particularly crucial in critical sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and smart cities.
The introduction of machine-to-machine (M2M) authentication will help to ensure that each IoT device has a unique identity and is authenticated before being allowed to send or receive data over the network.
4. More Intelligent IoT Solutions
A. Local Decision-Making with Edge Computing
The evolution of LoRaWAN-based solutions will also include the integration of edge computing capabilities. Edge computing refers to processing data closer to the source, reducing the need for constant communication with the cloud. This will enable devices to make real-time decisions locally without relying on cloud servers for every action.
For instance, a sensor in a smart farming application may detect a change in soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation systems locally without needing to send data back to the cloud for processing. This reduces latency and minimizes the strain on cloud infrastructure.
B. Machine Learning Integration
The incorporation of machine learning (ML) algorithms into LoRaWAN devices will enable devices to become more intelligent over time. These devices will be able to learn from their environment, detect patterns, and make decisions autonomously. For example, an industrial sensor might learn the normal vibration patterns of a machine and automatically alert maintenance staff if it detects unusual patterns that indicate a fault.
Partner with HashStudioz for Next-Generation LoRaWAN Solutions
At HashStudioz we specialize in crafting cutting-edge LoRaWAN-based IoT solutions that drive innovation across agriculture, supply chains, smart cities, and industrial monitoring.
Whether you’re looking to deploy smart irrigation systems, build predictive maintenance networks, or create secure, scalable logistics solutions, our team has the expertise and experience to make your vision a reality.
Let’s connect and transform your operations with intelligent, energy-efficient, and scalable IoT solutions!
Reach out to HashStudioz today and accelerate your IoT journey!

Conclusion
LoRaWAN technology is transforming the IoT ecosystem. In smart agriculture and supply chain management, it offers significant benefits such as long-range communication, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness.
By using LoRaWAN-Based Solutions, businesses can monitor critical processes, improve decision-making, and reduce operational costs. Real-world examples from industries worldwide show how powerful this technology can be.
As IoT adoption accelerates, LoRaWAN Solutions will play an even greater role in building efficient, resilient, and future-ready systems.