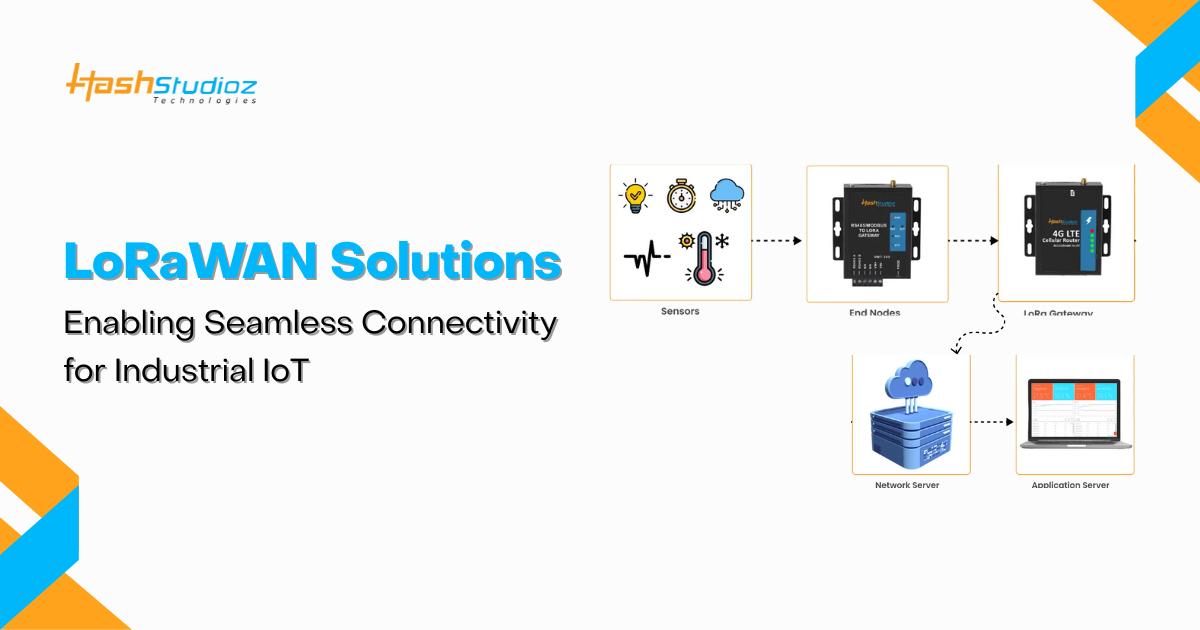
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming industries by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource management. At the heart of this transformation lies LoRaWAN-based solutions, offering a robust and scalable connectivity framework for IIoT applications. This article delves into the technical aspects of LoRaWAN technology, its benefits for industrial IoT, and how businesses can leverage these solutions to enhance operational efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Understanding LoRaWAN Technology
- Key Components of a LoRaWAN Network
- Benefits of LoRaWAN-Based Solutions for Industrial IoT
- Industrial Applications of LoRaWAN Solutions
- Implementing LoRaWAN Solutions in Industrial IoT
- Challenges and Considerations
- Future Prospects of LoRaWAN in Industrial IoT
- Partner with Experts: HashStudioz Can Help You Lead with LoRaWAN
- Conclusion
Understanding LoRaWAN Technology
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a low-power, wide-area networking protocol designed to wirelessly connect battery-operated devices to the internet over long distances. It operates in unlicensed radio frequency bands, making it cost-effective and accessible for various applications.
Key Components of a LoRaWAN Network
1. End Devices:
End devices are typically sensors or actuators that collect environmental or operational data and transmit it wirelessly using LoRa modulation. These devices are usually battery-powered, designed for low energy consumption, and can operate for years without maintenance. End devices can be configured as Class A, B, or C depending on their communication needs and energy constraints. They initiate communication with the network and are essential for applications like smart agriculture, industrial monitoring, and smart cities.
2. Gateways:
Gateways serve as the bridge between end devices and the network server. They receive LoRa signals from multiple end devices and convert them into IP packets to forward over the internet or private networks. Positioned strategically, gateways have long-range coverage, often spanning several kilometers. They are protocol-agnostic and do not decode the payload, maintaining low complexity. Their ability to handle messages from thousands of devices makes them critical in ensuring robust and scalable communication.
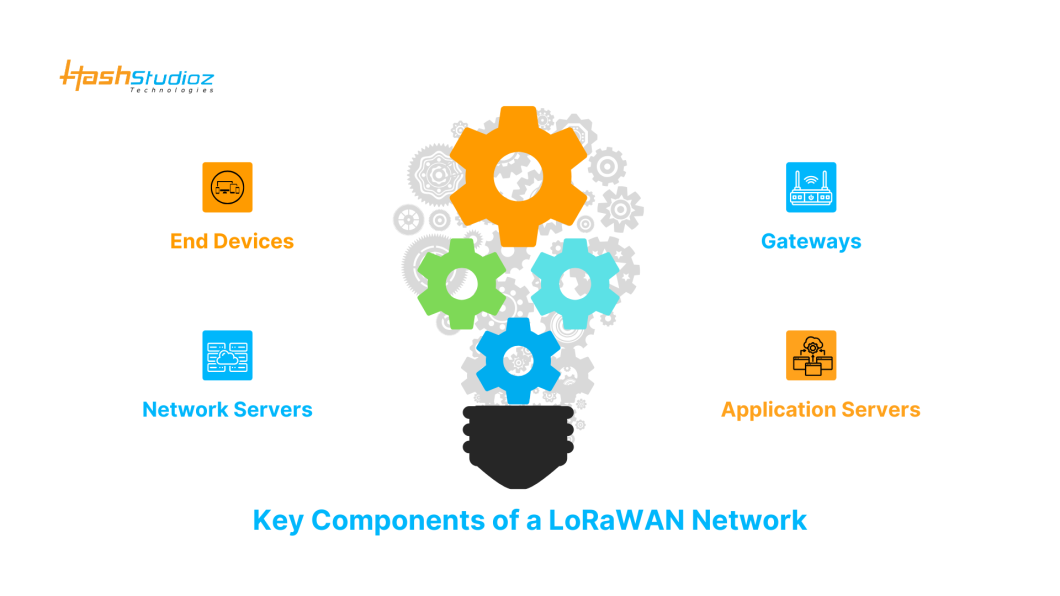
3. Network Servers:
Network servers play a central role in managing the LoRaWAN network. They authenticate end devices, handle packet deduplication, manage adaptive data rates, and ensure secure and reliable communication. The server filters and routes incoming data from gateways, applies security checks, and coordinates downlink responses. It also oversees network traffic to prevent congestion. The network server acts as a mediator, ensuring optimal performance by balancing communication loads and maintaining the integrity of transmitted data.
4. Application Servers:
Application servers process the data received from end devices, turning raw sensor inputs into meaningful insights. These servers decrypt the payload, extract relevant information, and integrate with business applications or dashboards for real-time monitoring and decision-making. They play a crucial role in end-user interaction by supporting alerts, analytics, and automated actions. In sectors like agriculture, healthcare, or logistics, application servers enable actionable intelligence, helping optimize operations and improve service efficiency through data-driven decisions.
Benefits of LoRaWAN-Based Solutions for Industrial IoT
1. Cost-Effective Connectivity:
LoRaWAN offers an economical alternative to traditional cellular networks, especially in remote or hard-to-reach industrial areas. It operates on unlicensed radio spectrum, eliminating licensing fees and reducing operational costs. The infrastructure is minimal—just a few strategically placed gateways can cover a vast area, significantly lowering deployment and maintenance expenses. This affordability makes it an attractive option for industries aiming to digitize operations without incurring high connectivity costs, particularly in large-scale outdoor or rural environments.
2. Enhanced Coverage:
LoRaWAN’s exceptional long-range capabilities make it ideal for industrial environments where standard wireless technologies fall short. It can transmit signals across several kilometers, even penetrating through thick walls, underground levels, and dense structures. This makes it highly suitable for sectors like mining, oil and gas, and manufacturing, where seamless connectivity in remote or obstructed areas is essential. The ability to maintain strong, reliable connections ensures uninterrupted monitoring and data flow, even in the most challenging industrial settings.
3. Battery Longevity:
LoRaWAN devices are engineered for ultra-low power consumption, allowing them to function for up to 10 years on a single battery. This feature is especially valuable in industrial IoT deployments where devices are scattered over large areas or located in hard-to-access spots. Long battery life reduces the need for frequent replacements or maintenance, saving both time and labor costs. It ensures long-term operation and reliability, making LoRaWAN ideal for monitoring assets that require minimal human intervention.
4. Real-Time Monitoring:
LoRaWAN supports continuous, low-latency data transmission from various sensors, enabling real-time monitoring of equipment, environmental parameters, and system performance. This capability enhances predictive maintenance, reduces downtime, and improves overall operational efficiency. Data collected can be analyzed instantly to detect anomalies, trigger alerts, or automate responses. Whether it’s monitoring temperature, pressure, vibration, or location, real-time insights empower industries to make faster, more informed decisions, boosting productivity and safety across operations.
5. Scalability and Flexibility:
LoRaWAN networks are inherently scalable and highly adaptable to the dynamic needs of industrial environments. As operations expand or change, additional devices and gateways can be integrated seamlessly without overhauling existing infrastructure. This flexibility allows businesses to start small and grow their IoT deployments as required, supporting thousands of connected sensors. Whether for a local facility or a globally distributed network, LoRaWAN ensures consistent performance, easy management, and room to grow with evolving technological demands.
Industrial Applications of LoRaWAN Solutions
1. Predictive Maintenance:
LoRaWAN enables predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring key equipment parameters such as vibration, temperature, and pressure. These sensors detect early signs of wear or malfunction, allowing maintenance teams to address issues before they lead to costly breakdowns or production stoppages. This proactive approach minimizes unplanned downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and improves overall operational efficiency. By leveraging real-time data insights, industries can transition from reactive to predictive strategies, ultimately reducing maintenance costs and enhancing productivity across manufacturing or heavy industrial operations.
2. Asset Tracking:
LoRaWAN provides reliable, real-time asset tracking across expansive industrial sites, warehouses, or outdoor locations. Devices attached to valuable equipment or inventory send regular updates on location and movement, improving visibility and control over physical assets. This helps prevent loss or theft, enhances inventory management, and supports efficient logistics planning. The long-range and low-power features of LoRaWAN make it particularly well-suited for tracking assets over large areas, even in remote or low-connectivity environments such as construction sites or shipping yards.
3. Environmental Monitoring:
Industrial environments often require strict monitoring of environmental parameters for compliance, safety, and process optimization. LoRaWAN sensors can continuously measure factors such as air quality, humidity, temperature, and gas levels. The data collected supports regulatory compliance, improves worker safety, and can trigger alerts in hazardous conditions. These solutions are especially useful in sectors like chemical manufacturing, mining, and food processing, where environmental control is critical. LoRaWAN’s low-power and long-range capabilities allow for cost-effective deployment in both indoor and outdoor settings.
4. Energy Management:
LoRaWAN-based solutions enable detailed tracking of energy usage across industrial systems, machinery, and buildings. By analyzing consumption patterns and detecting anomalies, businesses can identify inefficient operations and implement strategies to reduce energy waste. This not only cuts operational costs but also supports sustainability goals. Real-time energy data can inform load balancing, predictive analytics, and automated control of energy-intensive processes. The ability to deploy sensors without significant wiring makes LoRaWAN ideal for retrofitting older facilities with modern energy monitoring capabilities.
5. Smart Agriculture:
LoRaWAN technology plays a pivotal role in modern agriculture by enabling precise monitoring of soil moisture, weather conditions, irrigation levels, and crop health. These insights help farmers make data-driven decisions, such as when to water or fertilize crops, improving yield and resource efficiency. Its wide coverage allows connection across vast farmland, and long battery life means sensors can operate independently for years. LoRaWAN facilitates sustainable farming practices, reduces labor costs, and supports food production even in challenging rural environments.
Implementing LoRaWAN Solutions in Industrial IoT
Step 1: Assess Requirements:
Begin by thoroughly evaluating your industrial environment and operational needs. Identify the types of data to be collected—such as temperature, vibration, energy usage, or location—and determine the scale and complexity of your deployment. Consider the physical environment, including distance, obstacles, and potential interference. Understanding these requirements helps define the network architecture, sensor specifications, and data frequency. A clear assessment ensures the LoRaWAN solution aligns with business goals, regulatory needs, and performance expectations for successful implementation.
Step 2: Select Appropriate Devices:
Based on your requirements, choose LoRaWAN-compatible sensors and actuators that suit your operational conditions. Factors such as range, battery life, environmental resistance (e.g., waterproofing or temperature tolerance), and sensing capabilities should be evaluated. Whether for predictive maintenance, environmental monitoring, or asset tracking, selecting reliable, application-specific devices is crucial. The devices must support seamless integration with your network and deliver accurate, consistent data to optimize industrial processes and support long-term performance with minimal maintenance.
Step 3: Deploy Gateways:
Strategically install LoRaWAN gateways to ensure wide, uninterrupted network coverage across the facility or site. Gateways act as communication hubs between the end devices and network servers, so placement is key—ideally at elevated points or central locations to maximize range and minimize blind spots. Proper deployment ensures robust signal transmission, supports scalability, and enhances data reliability. For complex industrial terrains, deploying multiple gateways can provide redundancy and better manage data load from numerous connected devices.
Step 4: Integrate with Network Servers:
Configure network servers to manage data flow, enforce security protocols, and coordinate communication between gateways and end devices. These servers authenticate devices, decrypt messages, and filter duplicate packets to maintain data integrity. Additionally, they manage adaptive data rates to optimize transmission efficiency and battery life. A well-integrated network server setup ensures secure, efficient communication across the entire network, forming the backbone of your LoRaWAN solution and supporting continuous, real-time industrial operations.
Step 5: Analyze Data:
Connect your LoRaWAN infrastructure to application servers that process and analyze the incoming data. These platforms convert raw sensor readings into actionable insights using dashboards, analytics, and alert systems. Real-time analysis supports predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and faster decision-making. Historical trends can also be evaluated for long-term planning and efficiency improvements. By turning data into intelligence, application servers help industries enhance productivity, ensure compliance, and drive smarter, data-driven operations in an increasingly digital industrial landscape.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Interference
Operating LoRaWAN networks in unlicensed frequency bands poses a significant challenge due to potential interference from other wireless systems using the same spectrum, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. This interference can degrade signal quality, reduce data reliability, and affect communication range. To address this, effective network planning is essential, including channel selection, frequency hopping, and optimizing antenna placement. Deploying adaptive data rate (ADR) strategies and using spectrum analyzers during setup can also help mitigate interference and enhance network stability.
2. Security
Although LoRaWAN employs end-to-end encryption to secure data between end devices and network servers, additional security measures are vital to protect against evolving cyber threats. These include implementing secure authentication mechanisms, regularly updating firmware, and monitoring network traffic for anomalies. Ensuring strong key management practices and segmenting the network to contain breaches are also crucial. Industrial or critical infrastructure applications, in particular, demand heightened security to prevent unauthorized access and ensure data integrity across the communication chain.
3. Network Planning
Strategic network planning is fundamental for the successful deployment of a LoRaWAN system, especially in complex environments like factories or urban areas. Effective gateway placement ensures wide coverage and reliable data transmission, minimizing dead zones. Factors like building materials, terrain, and environmental interference must be analyzed during planning. Tools such as radio propagation models and site surveys can assist in optimizing network architecture. Moreover, scalability and redundancy should be considered to support future expansion and maintain consistent performance.
4. Device Management
Managing thousands of LoRaWAN devices across a network requires a comprehensive device management system. This system should support remote configuration, firmware updates, diagnostics, and lifecycle tracking. Automating these tasks reduces manual intervention and ensures devices remain functional and secure. Proper inventory management, coupled with performance monitoring, helps detect faults early and maintain operational efficiency. As the number of connected devices grows, efficient provisioning and decommissioning processes become essential to reduce downtime and enhance overall network sustainability.
Future Prospects of LoRaWAN in Industrial IoT
The adoption of LoRaWAN technology in industrial IoT is expected to grow significantly. According to ON World, the industrial IoT asset tracking market is projected to reach a quarter billion devices by 2027. As industries continue to embrace digital transformation, LoRaWAN-based solutions will play a pivotal role in enabling seamless connectivity and efficient operations.
1. Market Growth
The industrial IoT asset tracking market is poised for significant expansion, with projections by ON World estimating a deployment of over a quarter billion devices by 2027. This surge reflects increasing demand for cost-effective, low-power, and long-range connectivity, making LoRaWAN an ideal choice for industries seeking to optimize asset visibility and operational efficiency on a large scale.
2. Digital Transformation
As industries undergo rapid digital transformation, the need for reliable and scalable communication technologies intensifies. LoRaWAN supports this shift by enabling seamless integration of sensors and devices across vast industrial landscapes. It facilitates data-driven decision-making, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring, helping industries enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and achieve greater automation without relying on costly wired infrastructure.
3. Energy Efficiency and Scalability
LoRaWAN’s low-power capabilities make it particularly suited for industrial environments where battery-operated devices must function for years without maintenance. This energy efficiency, combined with its ability to support thousands of devices per gateway, ensures scalability for expanding operations. As industrial IoT ecosystems grow, LoRaWAN will continue to be a cornerstone technology for sustainable and scalable connectivity.
4. Enhanced Use Cases
Future advancements in LoRaWAN will unlock more advanced industrial use cases, such as smart logistics, environmental monitoring, and remote diagnostics. Integration with edge computing and artificial intelligence will further empower real-time analytics and autonomous operations. As standards evolve and interoperability improves, LoRaWAN will increasingly support complex, mission-critical applications across manufacturing, mining, oil and gas, and utilities.
Partner with Experts: HashStudioz Can Help You Lead with LoRaWAN
At HashStudioz, we specialize in delivering tailor-made LoRaWAN-based IIoT solutions for industries seeking to unlock operational efficiency, real-time monitoring, and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Whether you’re starting a small-scale IoT deployment or looking to scale a full-fledged industrial network, our team offers end-to-end services — from device integration to network setup and data analytics.
1. Custom IoT Hardware and Software Solutions
2. Expert Network Planning and Gateway Deployment
3. Advanced Data Analytics and Predictive Insights
4. Unmatched Security and Scalability
Ready to transform your industrial operations with LoRaWAN?
Contact HashStudioz today for a free consultation and discover how we can help you build a connected future!

Conclusion
LoRaWAN-based solutions offer a robust, scalable, and cost-effective connectivity framework for industrial IoT applications. By enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and efficient resource management, these solutions help industries enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. As the demand for connected devices grows, LoRaWAN technology will continue to be a cornerstone of industrial IoT infrastructure.
For businesses looking to implement LoRaWAN solutions, partnering with experienced providers and carefully planning the deployment can lead to successful integration and significant operational benefits.