In modern industrial networks, reliability and continuous connectivity are not optional—they are critical. Whether it is an automated production line, a smart grid component, or a remote surveillance system, network failure can lead to data loss, operational disruption, and high costs. This is where Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Routers come in.
A Dual SIM Profiling Router is a network device designed to manage two cellular SIM cards intelligently. It selects the best available network based on pre-set profiles or conditions. These routers are commonly found in industrial-grade hardware that can withstand environmental stress, provide cellular connectivity, and support secure data transmission.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Dual SIM Profiling Router?
- Internal Components and Architecture
- How Does a Dual SIM Profiling Router Work?
- Dual SIM Profiling vs Dual SIM Failover: Key Differences Explained
- Use Cases of Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Routers
- Advantages of Dual SIM Profiling Routers
- Key Performance Data
- Technical Considerations
- Recommended Dual SIM Profiling Router for Always-On Industrial Connectivity
- Why Choose HashStudioz for Industrial Router Solutions?
- Conclusion
What Is a Dual SIM Profiling Router?
A Dual SIM Profiling Router is a network router equipped with two SIM card slots and a profile-based routing system. This system determines how and when each SIM is used based on pre-defined parameters such as signal strength, data usage, cost, latency, or time of day.
These routers typically operate on 4G LTE networks, providing mobile broadband connectivity. The term Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Router refers to such routers built with industrial specifications—rugged casings, extended temperature ranges, ESD protection, and reliable uptime for long-term deployments.
Core Purpose
- Provide network redundancy
- Enhance uptime in mission-critical applications
- Enable failover between networks
- Support load balancing or link aggregation
- Offer policy-based routing for fine-grained control
Internal Components and Architecture
To understand how these routers work, let’s explore their technical makeup.
1. Dual SIM Interfaces
These routers have two SIM slots. Each slot can hold a SIM card from a different cellular provider. This enables network diversity and redundancy.
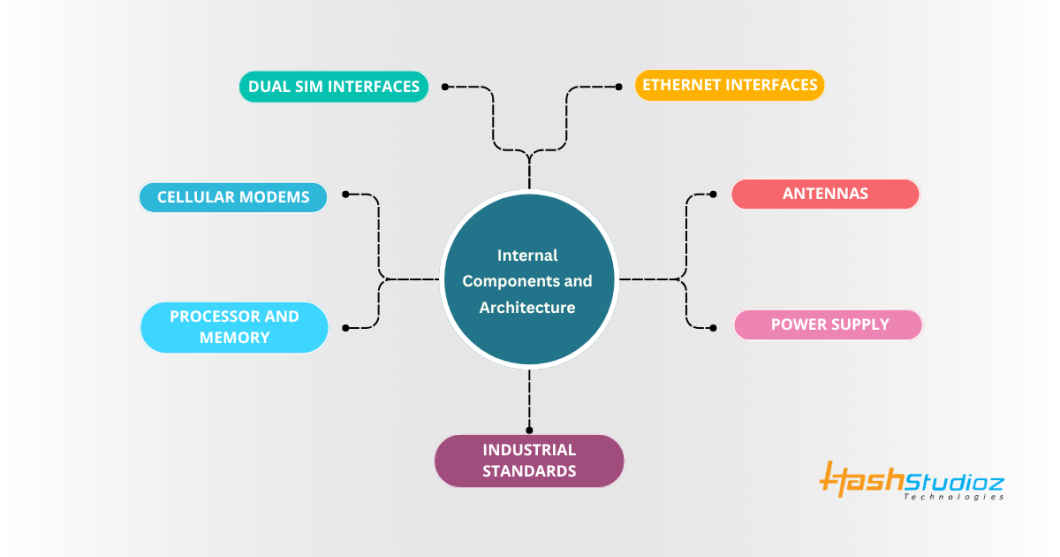
2. Cellular Modems
The router includes one or more 4G LTE modems. In most designs, a single modem switches between the two SIMs. In high-performance models, there are two separate modems, each dedicated to a SIM, enabling parallel usage.
3. Processor and Memory
An embedded CPU processes routing logic, SIM profiles, health checks, and firewall rules. RAM and flash storage support the operating system and configuration settings.
4. Ethernet Interfaces
Standard configurations include one WAN and one or more LAN ports. In industrial models, these are electrically isolated and designed to handle noise and surges.
5. Antennas
External antennas enhance signal reception. SMA connectors are commonly used for LTE and optional Wi-Fi.
6. Power Supply
Designed for wide voltage input (typically 9–36 V DC), these routers support environments with unstable or noisy power.
7. Industrial Standards
Housing is often metal, rated for extended temperatures (e.g., –40°C to +75°C) and certified against electromagnetic interference.
How Does a Dual SIM Profiling Router Work?
1. SIM Profiling Logic
At the core of the router’s functionality is the profile engine. This engine applies rules to determine how each SIM is used. Here’s how it typically works:
- Primary SIM is active by default
- Router constantly monitors network health metrics
- If thresholds are breached (e.g., low signal, high latency), the router activates the secondary SIM
- Traffic is switched, either fully or partially, based on the profile
2. Traffic Routing Methods
There are several routing strategies:
1. Failover Mode
- Only one SIM is active at a time
- When the active SIM fails (e.g., no network, high latency), the router switches to the backup SIM
- Ideal for cost-sensitive deployments
2. Load Balancing Mode
- Both SIMs can be active
- Traffic is divided between the two based on load
- Useful for bandwidth-intensive applications
3. Bonding Mode (in some models)
- Both connections are aggregated into one logical link
- Increases bandwidth and provides redundancy
- Requires bonding-capable infrastructure
4. Profile-Based Routing
- SIM selection based on traffic type, IP range, time of day, or data usage
- Offers precise control over routing behavior
Dual SIM Profiling vs Dual SIM Failover: Key Differences Explained
Though often used interchangeably, Dual SIM Profiling and Dual SIM Failover represent two distinct functionalities in industrial routers. Understanding the difference is critical when selecting or configuring a Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Router.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dual SIM Failover | Dual SIM Profiling |
| Function | Backup connectivity | Intelligent, rule-based routing |
| Active SIMs | One SIM active at a time | One or both SIMs can be active |
| Switching Trigger | Link failure, signal loss, or timeout | Conditional logic (data usage, time, traffic) |
| Routing Logic | Reactive (after failure) | Proactive (based on predefined profiles) |
| Configuration Complexity | Low | Medium to High |
| Control Over Traffic | Minimal | High |
| Data Plan Optimization | No | Yes |
| Latency Handling | Delays during switch | Can preemptively switch based on thresholds |
| VPN and Security | Usually supported | Usually supported |
| Use Case Example 1 | POS terminals needing backup connectivity | Fleets needing separate traffic paths |
| Use Case Example 2 | Remote sensor sites with single uplink | Industrial routers managing data limits |
| Best For | Redundancy and high uptime | Traffic management, cost control, performance |
Use Cases of Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Routers
1. Remote Monitoring Systems
In oil fields, water treatment plants, or mines, wired connections are often unavailable. Dual SIM routers offer resilient connectivity, ensuring critical data reaches control centers without interruption.
2. Smart Grids and Energy Systems
Power substations use these routers to communicate SCADA data. Failover ensures operational continuity even during primary network outages.
3. Point-of-Sale (POS) Networks
Retail chains use these routers to maintain payment connectivity. A secondary SIM ensures no downtime, even if one network fails.
4. Transportation and Fleet Vehicles
Mounted in buses or trucks, these routers provide real-time GPS tracking, diagnostics, and passenger Wi-Fi with cellular redundancy.
5. Industrial Automation
Factories and plants use dual SIM routers for machine-to-cloud communication. Failover protects against network interruptions, avoiding costly downtimes.
Advantages of Dual SIM Profiling Routers
- High availability: Reduces network downtime
- Cost efficiency: Use cheaper SIM for regular data, backup SIM only when needed
- Network flexibility: Use SIMs from different carriers for maximum coverage
- Remote management: Monitor and manage routers without on-site access
- Security: Many models include VPN support, firewalls, and access controls
Key Performance Data
- LTE Speed (Cat-4): Up to 150 Mbps download, 50 Mbps upload
- Failover time: Often between 100 ms to 2 seconds depending on model
- Temperature Range: –40°C to +75°C (industrial models)
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Typically above 100,000 hours
- Power Input Range: 9–36 V DC standard in industrial applications
Technical Considerations
1. Configuration
Router profiles must be accurately defined to avoid unintended SIM switching or unstable connections. Misconfigured DNS, NAT, or routing tables can disrupt communication paths. MTU settings should align with LTE standards to prevent packet loss and VPN connectivity issues.
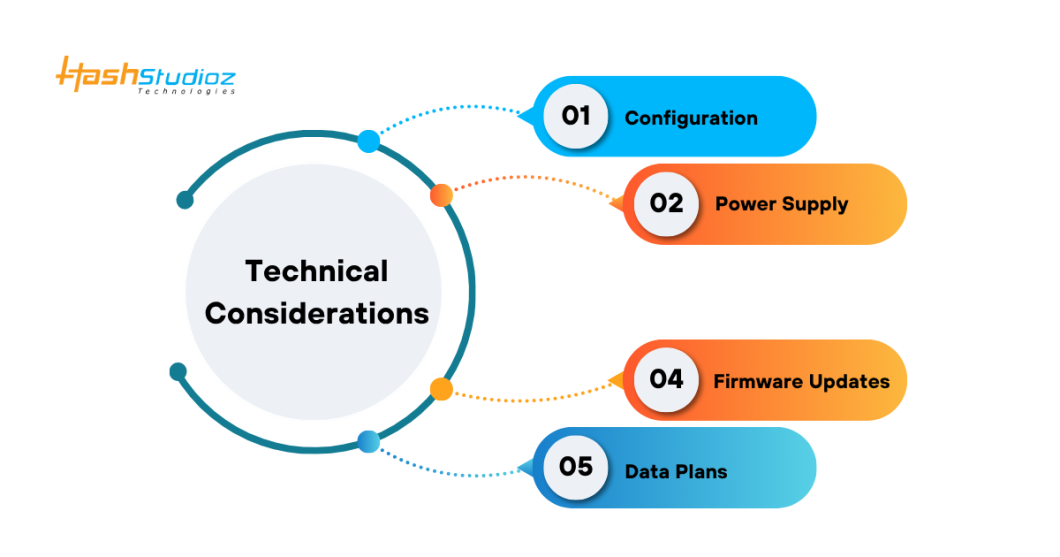
2. Power Supply
A consistent power source is essential, especially during SIM switching. Voltage drops or unstable inputs may trigger unexpected reboots. In solar-powered systems, routers must operate efficiently under limited energy conditions to maintain uptime during battery-only or low-light operation periods.
3. Firmware Updates
Regular firmware updates are crucial for maintaining security and functionality. Remote update capability is important for managing routers deployed in the field. Devices should also support rollback to a previous version in case an update causes operational failure.
4. Data Plans
Each SIM in a dual SIM 4G LTE industrial router must have an active data plan. To control costs, administrators should enable data usage profiling, allowing for smart selection between SIMs based on consumption limits, traffic type, or network cost.
Recommended Dual SIM Profiling Router for Always-On Industrial Connectivity
For businesses that rely on continuous network access, selecting a router with intelligent SIM management is key to minimizing downtime and maintaining seamless operations.
The Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Router from IoTStudioz is designed with dual SIM profiling technology, which actively monitors network performance and automatically routes traffic through the best available cellular connection. This proactive approach ensures uninterrupted connectivity, even in areas with fluctuating signal strength or multiple network operators.
Built for demanding industrial environments, this router supports reliable communication for applications such as remote monitoring, industrial automation, smart utilities, logistics tracking, and other mission-critical operations. Its robust construction, secure connectivity features, and intelligent failover capabilities make it an ideal choice for businesses that cannot afford network interruptions.
Power Your Network with a Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Router
Why Choose HashStudioz for Industrial Router Solutions?
At HashStudioz, we provide custom industrial IoT solutions that integrate Dual SIM 4G LTE Industrial Routers into mission-critical infrastructure. Whether your business operates in logistics, energy, automation, or surveillance, our team delivers:
- Custom firmware and router configurations
- Full remote monitoring dashboards
- Carrier profile optimization
- Edge computing integrations
- Long-term support and updates

Conclusion
As industries become more reliant on remote systems, automation, and data connectivity, the importance of reliable networking increases. Dual SIM profiling routers serve a vital role in providing that resilience, especially where wired networks are not feasible or reliable.
For engineers, network architects, or IT administrators deploying industrial solutions, choosing the right dual SIM 4G LTE industrial router—and configuring it properly—can make the difference between stable performance and operational failure.

